spinal compression test|jackson compression test vs spurling's : manufacture Depending on the cause of spinal cord compression, symptoms may develop slowly or quickly. Some injuries may cause immediate symptoms. Some health conditions—such as a tumor or infection—may cause symptoms that come on gradually over days or even weeks. Wear and tear of the spine . See more webA mostra Mundo Pixar inicia em Porto Alegre, no BarraShoppingSul, com 13 salas baseadas no universo Disney Pixar, como Toy Story, Luca e Lightyear. Os ingressos podem ser .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webThis version of Batman is called "The Goddamn Batman" to distinguish him from his mainstream counterpart. Some also call him "Crazy Steve" thanks to Atop the Fourth .
what is deep neck compression
thickness measuring crossword
Depending on the cause of spinal cord compression, symptoms may develop slowly or quickly. Some injuries may cause immediate symptoms. Some health conditions—such as a tumor or infection—may cause symptoms that come on gradually over days or even weeks. Wear and tear of the spine . See moreTo make a diagnosis, your healthcare provider will ask questions about your symptoms and do a complete physical exam. The exam will look for signs that indicate spinal compression, . See moreSpinal cord compression has numerous possible causes. In some cases, however, compression can come on suddenly and no known cause can be determined. Potential causes of . See moreTreatment for spinal cord compression depends on the cause and the type of symptoms you are experiencing. Many cases of spinal cord compression do require surgery, but in mild cases, your healthcare provider may recommend non-surgical therapies to decrease pain and improve your quality of life, such as medication and physical therapy. See more
The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when .
Key Points. Various lesions can compress the spinal cord, causing segmental sensory, motor, reflex, and sphincter deficits. Diagnosis is by MRI. Treatment is directed at relieving compression. (See also Overview of Spinal Cord . The Spurling test is one of the best-known and most widely used provocative tests for the assessment of the cervical spine. The Spurling test was originally named as Spurling’s . The Spurling test helps to diagnose cervical radiculopathy. It’s also called the Spurling compression test or Spurling maneuver. The Hoffman test, also known as the Hoffman sign test, lets your doctor know whether there are compression — or pressure — problems in your spine near your neck.
After the initial examination, each subject, while seated, underwent six distinct provocative maneuvers of the cervical spine in the following order: lateral bending and axial compression, the original test described by Spurling and Scoville ; .
Spurling's test involves compression of the cervical spine while it is slightly extended, rotated, and tilted toward one side. In a positive test, pain radiates distally, usually in a radicular .Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a neck condition that occurs when the spinal cord becomes compressed—or squeezed—due to the wear-and-tear changes that occur in the spine as we age. The condition commonly occurs in .Most people with back pain consult their primary health care provider first. The doctor will begin with a thorough medical history and physical exam. If a doctor believes a spinal compression fracture may be present, the following tests may be ordered:X-rays are usually the first tests ordered; they can show which bones have fractured.
special test for cervical spine
Flexion compression test. Procedure: The patient is seated. The examiner stands behind the patient and passively moves the cervical spine into flexion (tilts the patient’s head forward). Then axial compression is applied to . The test has also been referred to as the Foraminal Compression Test, Neck Compression Test, or Quadrant Test. The Spurling test is considered a provocative test used in the spinal examination. In several previous trials (mostly conducted in the late 1900’s), the test had proven to have high specificity, but low sensitivity. Cervical myelopathy is a common degenerative condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness in hands and gait imbalance. ORTHO BULLETS Free CME. Join now Login. Select a Community . test is positive when extreme cervical flexion leads to electric shock-like sensations that radiate down the . (2,3) The test is most commonly defined in current literature as passive cervical extension, ipsilateral rotation, and axial compression. (4) This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients with cervical radiculopathy and other upper extremity nerve pathologies.
The foraminal compression test or Spurling's test is statistically the best provocative test for confirming the diagnosis of cervical radiculopathy, when performed properly. It is performed by extending the neck and rotating the head and then applying downward pressure on the head. . Ramifications of a positive cervical spine clearing test .
Severe compression of the spinal cord can result from traumatic injury, spinal infection or other conditions. When the spinal cord compresses, it can lead to a variety of symptoms, called myelopathy. There are different types of myelopathy — cervical, thoracic and lumbar. The location of the spinal compression determines the type. Thank you for following @OrthoEvalPal Today I will show you how to perform the Cervical Compression Test correctly and what you should see in a positive tes.
Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) are the most common complication of osteoporosis, affecting more than 700,000 Americans annually. 1 Patients with VCFs account for 66,000 physician office .• Cervical Flexion Rotation Test • Cervical Compression, Jackson’s Compression, Maximum Foraminal . roots, spinal nerves, and the brachial plexus, and may also decrease intraforaminal pressure. Interpretation The sign, when it reduces peripheral symptoms in the upper extremity, is suggestive of cervical radiculopathy. The presence of .A cancerous tumor in your spine may cause bone pain, compression fractures or affect how your spinal cord works. Treatment varies but typically emphasizes managing symptoms and slowing down tumor growth. . Bone scan: This test may detect abnormal areas in your spine that may be signs of spinal metastasis.Fractures of lumbar vertebrae occur in the setting of either severe trauma or pathologic weakening of the bone, see image R L4 compression fracture.. Osteoporosis is the underlying cause of many lumbar fractures, especially in postmenopausal women.; Osteoporotic spinal fractures are unique in that they may occur without apparent trauma. Any injury that changes .
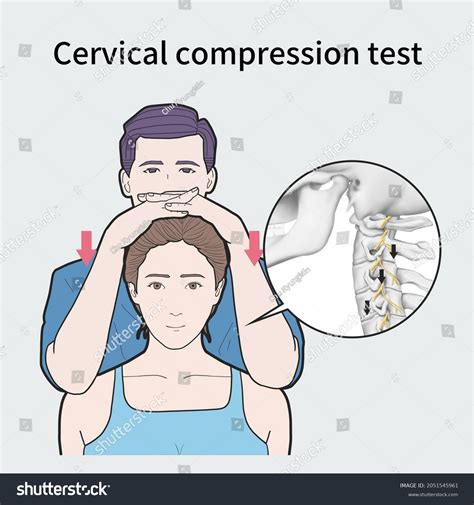
After the initial examination, each subject, while seated, underwent six distinct provocative maneuvers of the cervical spine in the following order: lateral bending and axial compression, the original test described by Spurling and Scoville ; lateral bending, ipsilateral rotation and axial compression, also called the maximum cervical .Purpose of Test: To identify the effect of vertebral compression to the patient’s symptoms. Test Position: Sitting. Performing the Test: Apply an inferiorly directed pressure through the superior aspects of both shoulders. A positive response is an indication of pain. Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown. Importance of Test: With a reproduction of pain, it could signal tissue trauma, .
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of one or more spaces within your spinal canal. It causes symptoms like back or neck pain and tingling in your arms or legs. . You can feel symptoms of cervical spinal stenosis anywhere below the point of the nerve compression in your neck. Symptoms include: Neck pain. Numbness or tingling in your arm, hand . Spinal stenosis refers to a narrowing of the vertebral canal, which can occur at any level. The narrowing can compress on nerve tissue that travels through the spine and cause pain, often in the lower back or neck. Spinal stenosis most commonly occurs in the lumbar spine than the cervical spine. Studies have reported an incidence of 1 in 100 000 for cervical spine . Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with hip flexion, abduction, and external rotation. . SI compression test. performed with patient laying lateral on exam table. medial directed force applied over the iliac crest on the affected side.Chronic compression develops over months to years. It is commonly caused by. Bony protrusions into the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spinal canal (eg, due to osteophytes or spondylosis, especially when the spinal canal is narrow, as occurs in spinal stenosis) Compression can be aggravated by a herniated disk and hypertrophy of the ligamentum .
A compression fracture of the spine that appears for little or no reason may be the first indication that an unrecognized cancer has spread to the spine. . If a vertebral compression fracture is suspected, the doctor will test for tenderness and sensitivity near specific vertebrae along the spine. Based on the patient's history and physical .If a vertebral compression fracture is suspected, the doctor will test for tenderness and sensitivity near specific vertebrae along the spine. Based on the patient's history and physical exam, if a vertebral fracture is suspected, an x-ray will be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.The Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) Compression Test or “Approximation Test” is a pain provocation test which stresses the SIJ structures, in particular, the posterior SIJ ligament, to attempt to replicate patient’s symptoms (Laslett and Williams; . Spine. 1995 Jan 1;20(1):31-7. foraminal compression test that is specific, but not sensitive, in diagnosing acute radiculopathy. performed by rotating head toward the affected side, extending the neck, and then applying and axial load (downward pressure on the head) . for cervical spinal cord compression and myelopathy. test is positive when cervical flexion or extension .
Pages in category "Cervical Spine - Special Tests" The following 11 pages are in this category, out of 11 total. B. . Canadian C-Spine Rule; Cervical Distraction Test; Cervical Flexion-Rotation Test; Cervical rotation lateral flexion test; Cranio‐cervical Flexion Test; H. Hoffmann's Sign; S. Sharp Purser Test; Spurling's Test; T. Transverse . Spinal nerve compression symptoms resemble those of many other nerve-related conditions. You should get an expert opinion on the cause of your nerve symptoms to receive the most appropriate treatment. Many types of doctors can perform a physical evaluation, but a neurologist specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions involving the nervous system.
Therefore, when making the diagnosis of spinal stenosis, your healthcare provider will be looking for signs of compression in and around the spinal canal. Below are some of the test commonly used to help make the diagnosis of spinal stenosis. . A bone scan is not a test that will detect spinal stenosis, but it can be helpful to look for . Degenerative cervical myelopathy is the most common degenerative, nontraumatic, and progressive form of spinal cord compression worldwide. 3, 10, 13, 14 It is also recognized as the leading cause .

A new music service with official albums, singles, videos, remixes, live performances and more for Android, iOS and desktop.
spinal compression test|jackson compression test vs spurling's